Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is a disease that affects females in their reproductive system. The major cause of this disease can be regarded as a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI). However, if you were able to diagnose the sexually transmitted infections first-hand, you are less likely to develop the stage of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID).
If the infection stays in the body of the individual for a longer period of time, without getting timely treatment, it may turn into PID. There are a lot of people who assume yeast infection is the major cause of their PID. But the fact is that a yeast infection could only worsen the intensity of a PID but cannot be the direct cause of the same. This article discusses the relationship between Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases and yeast infections that are commonly found in females.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Causes And Symptoms
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is caused by bacteria entering the reproductive tract, passing through the cervix and into the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Common infections include gonorrhea and chlamydia, which cause 90% of PID cases. Symptoms include pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, sex-related pain, burning during urination and irregular periods.
Causes Of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
1. Bacterial STI
If yeast infections cannot be the direct cause of Pelvic Inflammatory disease, it is important to know what actually causes this condition. According to a lot of medical studies and research conducted on the topic reveal that it is the bacterial infection left out from an STI that causes the same. Not all bacterial STIs do not become the cause of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. You may check for the following bacterial names in order to assume it as a root cause of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) such as; Chlamydia, Mycoplasma Genitalium, and Gonorrhea. Syphilis is also a bacterial STI, however, this does not become the reason behind your PID. however, once you are diagnosed positive with PID, it is important to understand that your vulnerability towards infections such as Syphilis and HIV is at an elevated risk. Viral and parasite-caused STIs such as HIV, Herpes Simplex Virus, and HPV also do not take responsibility for your Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. On account of these complex interrelations between selective bacterial STIs and PID, most doctors may advise you to have a detailed checkup once you are diagnosed with either any kind of STI or PID in the first place.
2. Bacterial Infection Of The Vaginal Tract
Your vaginal tract can also get infected by causes other than unprotected sexual intercourse. Some of them include vaginal delivery and miscarriage. During these events, it is highly likely that many inflammation-causing bacteria get inside the reproductive tract. These may remain undiagnosed and eventually lead to the development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
3. Cervical Medical Procedures
If you have undergone any medical procedures involving the exposure of the cervix, it may again increase your risks of getting infected with Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Cervical Cancer Screening and the insertion of any kind of intra-uterine devices can be regarded as such procedures. Any possible failure in the hygiene protocol that needs to be followed during these processes can also be a significant reason behind the contraction of PID.
Symptoms Of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
As we have already mentioned, untreated Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) can be the major cause of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), it is important to have a clear and comprehensive understanding of the symptoms of the same so that you will not reach further complications of it. Here are some of the symptoms that may help you suspect Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) and seek medical help as soon as possible.
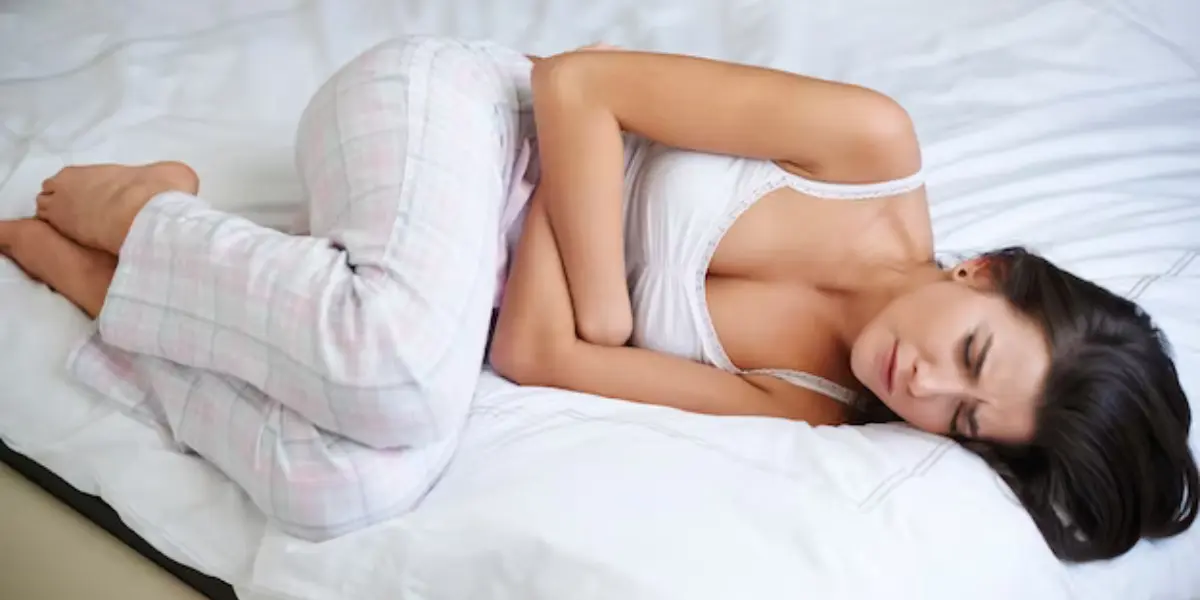

1. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain can be a common symptom in women in their reproductive ages, especially during the premenstrual and menstruating periods. However, if the abdominal pain happens towards and after the end of a regular menstrual cycle, you may better suspect the chances of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). If the abdominal pain is only experienced on a single side, you may assume a greater chance for PID.
2. Bleeding Differences
If you are contracted with Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, you are highly likely to have menstrual bleeding with an unusual colour. Apart from the colour, the odour of the blood may also change to something bad and pungent. The same happens with the white discharge that you may experience during times other than the menstrual cycle. Odour and colour changes in white discharges can also be considered a valid symptom of PID. An irregular menstrual cycle may also indicate the same.
3. Fever While Menstruating
If you are experiencing a mild rise in the body temperature, it may indicate that your Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) has reached its more severe stage, when the infection has become contagious. The abdominal pain that you may experience after the menstrual cycle, particularly on one side may also get worse in this stage. Along with fever, the patient may also experience nausea and vomiting, making each menstrual cycle quite challenging for them. During this stage, the vaginal discharge may look similar to puss and appear in shades ranging from yellow to light green.
4. Pain During Sexual Intercourse
Pain during sexual intercourse can be caused due to a lot of reasons and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease can also be one among them. Hence if you are experiencing the symptoms along with the pain during sexual intercourse, you may strongly suspect the contraction of PID. Patients may also experience pain during urinating.
These symptoms are highly beneficial for expert medical practitioners to identify the bacterial infection that has caused that particular case of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Patients with milder symptoms are highly likely to be infected with bacteria such as Chlamydia and Mycoplasma genitalium. On the other hand, if the patient is experiencing severe symptoms, Gonorrhea might be the cause. That is why it is important that you observe the symptoms carefully, so you can help your doctor with an accurate diagnosis.
Also Read:- How To Stop Vaginal Itching? 7 Home Remedies For Vaginal Yeast Infection
Summarization
So, to put it in a nutshell, yeast infections do not primarily cause Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). Bacterial infections are the major cause of PID and those infections can happen in a lot of different ways. However, one of the most important ways through which bacteria enter into the reproductive tract of females is through unprotected and unhygienic sexual intercourse. Some medical procedures and biological events may also cause the pathogens to enter the tract and make it infected. If your reproductive tract is already infected with any kind of yeasts, you are more vulnerable to PID, even though it does not become a direct cause.
References:
- Kim S, et al. (2021). Characteristics of vaginal microbiome in women with pelvic inflammatory disease in Korea.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8458998/ - Overview. (2022).
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pelvic-inflammatory-disease-pid/ - Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – CDC detailed fact sheet. (2021).
https://www.cdc.gov/std/pid/stdfact-pid-detailed.htm