Cirrhosis of the liver, or in simple language, chronic liver disease is the fastest-growing global health burden. According to the epidemiological studies conducted by the National Library of Medicine, cirrhosis caused almost 1.48 million deaths in 2019. This number has increased to 1.8% as compared to 2017, when it was just 5.2 million. This article focuses on the symptoms, causes, and treatment of liver cirrhosis in detail to define it with ease.
What Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver? Keep Your Liver Healthy
Before you know the causes and symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver, it is essential to understand its term first. Well liver cirrhosis is a progressive disease that is caused when healthy tissues are replaced by scar tissues that gradually damage the liver. This damage can affect the blood flow throught the liver, which may also lead to dysfunction of the organ and even death.
Chronic liver disease (CLD) can be caused due to viral infections such as hepatitis B and C or sometimes genetic diseases. Among them, the main cause is long-term alcohol consumption, which can damage the liver cells over the years. If you want to understand the culprit behind CLD, it is essential to identify its symptoms before it gets chronic.
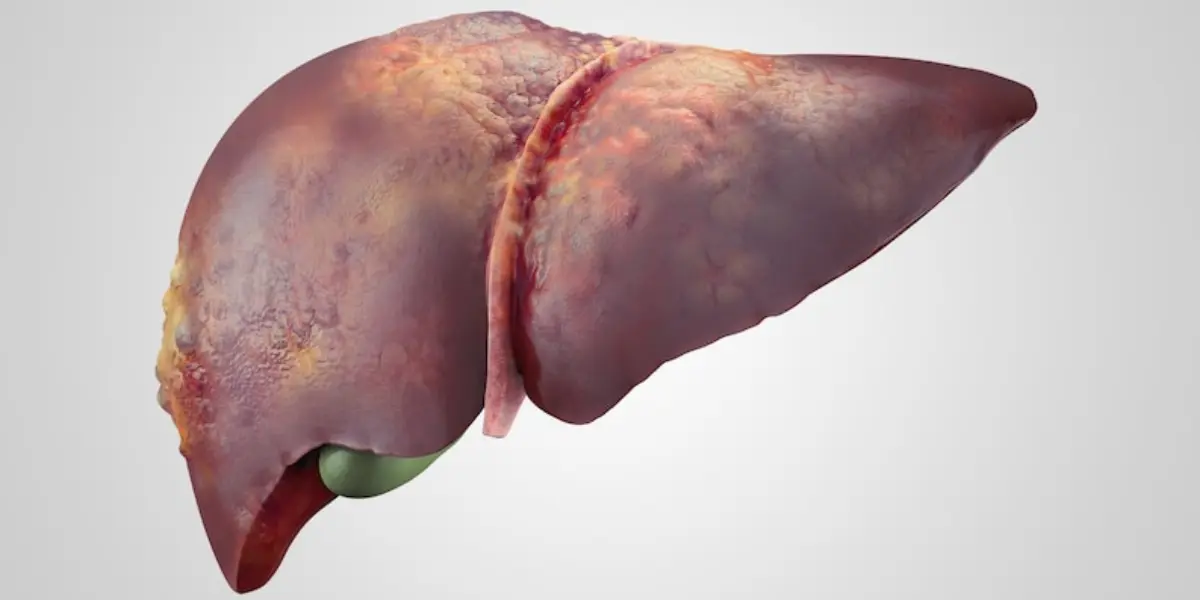
How To Find Out If A Person Has Liver Cirrhosis?
Well, it is difficult to notice the symptoms of cirrhosis in the initial stage as it is progressive in nature. The signs start occurring only when the liver stops functioning properly. Therefore, CLD has been categorized into two stages that are hard to track for the common people.
The first stage is the compensated stage, which is also called asymptomatic, which means showing no symptoms. It is the initial stage of scarring on the liver, which has not spread enough to damage the organ. Unfortunately, it can’t be tracked due to unnoticeable reactions in the body and may turn chronic soon.
The second stage is decompensated, where you can find serious symptoms that can be cured only by medical treatment. This stage usually occurs when the liver is unable to purify the blood, and fat and fat-soluble vitamins start settling in the liver. Initially, it can be managed in the first phase, and the individual can be revised to compensate with proper treatment.
Some of the common symptoms that can be seen in the decompensated stage are as follows:
- The person may experience uncertain fatigue.
- They may also experience mild pain in the upper right side of the stomach.
- An individual may start losing the muscles.
- Can have enlarged or swollen veins
- Even experiencing an increase in appetite; sometimes, nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Yellow discoloration appears in the skin and eye.
- Frequent bleeding while brushing.
- Itchiness in the skin without any rashes.
- Dark color urine with tarry stool
- Sometimes, confusion or facing difficulty in thinking.
What Are The Common Causes Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver
You can find various different causes of liver cirrhosis, among which chronic alcohol misuse and hepatitis are the most common ones. Talking about the first reason for CLD, alcohol consumption may cause both men and women but in different situations. For the male liver, the intake of more than one drink in a day can increase the risk of cirrhosis, while consumption of alcohol at any level in women may cause CLD.
Another reason is hepatitis B and C, which can lead to inflammation or serious damage to the liver. Individuals who are using illegal drugs or involved in sexual activities without any protection are at higher risk of viral hepatitis. A person going through kidney dialysis can also get infected by chronic liver disease.
In some cases, nonalcoholic individuals can also be affected by cirrhosis of the liver. It can be caused due to fat buildup in the liver. This condition is mainly called Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NFLD) in medical terms. This fat buildup may cause liver damage and inflammation, leading to the situation of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (SASH), which can cause cirrhosis.
What Are The Treatment Available For Chronic Liver Diseases?
As you might have understood now, cirrhosis of the liver shows late symptoms. This means liver cirrhosis gets notified only when it becomes chronic and can be treated only by professionals. The person may go through various routine checkups to find out the cirrhosis of the liver.
While visiting the doctor, it is essential to be honest about your lifestyle and any type of medication. It is because the healthcare professional may ask you about alcohol misuse, family history, or any other risk factors. After knowing these factors, the doctor may check you physically such as if your eyes and skin are turning yellow or reddened palm.
After testing these symptoms, the doctor may ask for a blood test to measure the liver products like liver enzymes and bilirubin levels. The next stage is the screening, which includes CT and MIR scan, and last is the liver biopsy to determine the cause of causes. After this, the healthcare profession can recommend medication if it can be cured or even a liver transplant if the situation is chronic.
Also Read:- How Can I Improve My Liver Function Fast? Reboot Your Liver
Final Words
Chronic Liver Disease (CLD) is one of the serious health issues recognized globally to mitigate its symptoms. Therefore, government bodies and even private institutes are trying to fight against this chronic disease while spreading awareness of less consumption of alcohol. Some new research is also being conducted to notice its issues in the initial stage.
Till then, as an individual, you can tackle this issue by improving your lifestyle by following a proper diet. Make sure you enjoy your glass of wine at a moderate level and follow your medication properly, if any.
References:
- Cirrhosis. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/cirrhosis. Accessed Jan. 5, 2023.
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Cirrhosis: A Patient’s Guide (https://www.hepatitis.va.gov/cirrhosis/patient/index.asp). Accessed 7/26/2023.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, U.S. Cirrhosis (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/cirrhosis). Accessed 7/26/2023.