Atherosclerosis refers to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the walls of the arteries. They are made up of deposits of LDL cholesterol ( the bad cholesterol), then of limestone and inflammatory and muscle cells surrounded by fibrous layers. These atheromatous plaques grow in the walls of the arteries which thicken and become stenotic (reduction in the caliber of the arteries, we say that the lumen of the artery is narrowed). Atherosclerosis mainly affects medium and large arteries: the coronary artery which irrigates the heart, the internal carotid and vertebral arteries intended for the brain, the infrarenal abdominal aorta, the iliac artery, the femoral artery, the popliteal bones of the leg. This article would like to examine in detail the term atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis: Types
Atherosclerosis can be classified into six types according to histological classification.
- Type 1: Adaptive intimal thickening that obstructs the lumen Inna fixed position from birth
- Type 2: Macrophage foam cells and lipid-rich smooth muscle cells (fat streak)
- Type 3: This stage is intermediate between type 2 and type 4 and Symptoms appear at this stage
- Type 4: At this stage, a lipid core is formed
- Type 5: At this stage, calcification occurs and the lipid core contains thick fibrous layers
- Type 6: There may be tears, hematomas, or blood clots.
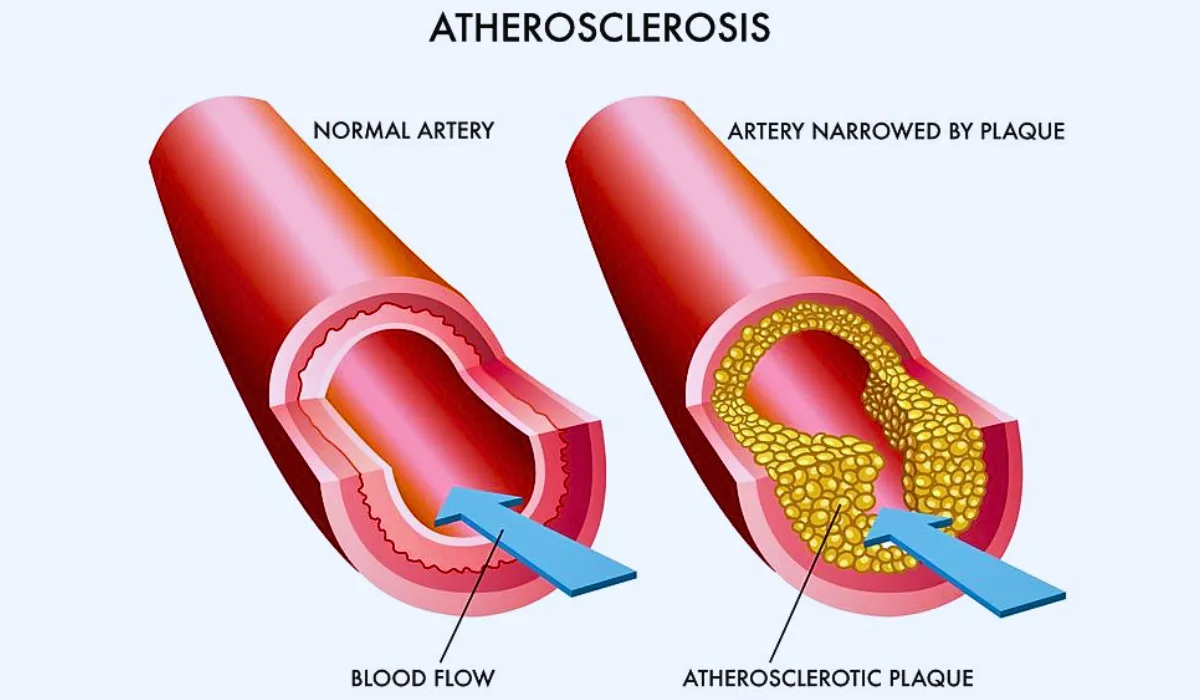
Symptoms
Atherosclerosis is a disease that develops gradually and silently. It is the consequences of the obstruction which will cause symptoms. Symptoms vary depending on which arteries have atherosclerosis. The narrowing of an artery of the heart manifests itself by progressive shortness of breath during exercise ( unstable angina) obliterating arteries of the lower limbs by muscle cramps in the calves during exercise, in the event of a rupture of atherosclerotic plaques, the Symptoms are noisy, chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating in the event of myocardial infarction, weakness on one side of the body, arms or legs, difficulty speaking, disturbance balance, Intense headache in case of stroke.
Causes
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disease, for Low-Density Lipoprotein to accumulate in the artery’s walls, the endothelium which serves as the protective layer that lines the lumen of the arteries can be compromised by reckless lifestyle. The damaged endothelium becomes permeable to the cholesterol which will penetrate the walls of the arteries and cause a cascade of inflammatory reactions altering the functioning of the artery and initiating the synthesis of atherosclerotic plaques, the artery will thicken, harden, and become less flexible.
Diagnostic
The doctor performs a questioning and clinical examination of the patient suspected of atherosclerosis. This involves detecting family history, observing all the risk factors known as cardiovascular risk factors presented by the person, and looking for cardiovascular warning signs.
The diagnosis of atherosclerotic plaques and their hemodynamic impact is made with imaging, an ultrasound initially for the
Carotid and vertebral arteries, the aorta and its branches ( arteries of the arms, digestive, and renal arteries, arteries of the leg)
CT angiography or MRI angiography are second-line examination to most often discuss revascularization
Treatment
The treatment of atherosclerosis combines lifestyle rules and medication, a healthy lifestyle is fundamental. In terms of diets, it is advisable to limit saturated animal fats, by consuming a lot of fruits and vegetables which facilitates the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and provides Vitamin K which protects against aging of the arteries. Salt consumption should not exceed 5g per day. Stopping smoking is essential because tobacco is responsible for arterial spasms and leads to the production of oxidative free radicals which will attack the arteries.
Other fundamental measures:
Practice physical activities, sleep well, and manage stress. In addition to these lifestyle measures, three treatments are prescribed in the event of atheromatous disease. First of all, antiplatelet agents if the atherosclerotic plaques are formed. The second drug is statins, this drug has a way of making the atherosclerotic plaques stable, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and limits the absorption of LDL cholesterol.
The last drug treatment consists of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist. This blocks the endocrine system involved in the development of the disease.
Prevention
The prevention of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases for which it is responsible is based above all the prevention of risk factors which would be in 8 out of 10 accidents. It is important to know and control your blood pressure, your diabetes, and your cholesterol level while adopting a healthy lifestyle. You must avoid tobacco, practice regular physical activity, adopt a low-fat diet, monitor your weight, your alcohol consumption, and reduce your stress level. The longer these lifestyles are implemented the better, as lipids streak (the beginning of atherosclerotic plaques) can appear in the arteries during the first 20 years of life.
Home Remedies for atherosclerosis
- Fast for several days under medical examination
- Diet of freshly squeezed vegetable juice from a juice extractor (carrot and green vegetable like the cabbage family)to which marine magnesium is added + one tablespoon of dehydrated barley grass juice powder + 5 drops of vitamin D + 2 capsules per meal of Omega-3 or teaspoon of flaxseed oil in your daily diet.
- Significantly reduce or even eliminate alcohol consumption, eliminate unwanted snacks between meals, and reduce the consumption of sugar, excess of which promotes an increase in certain saturated fatty acids which prove to be harmful foods contributing to atherosclerosis. Ideally, only consume foods of organic origin, healthy, unrefined, and from the season and region. Avoid fried food.
Conclusion
In conclusion, atherosclerotic plaques gradually block the arteries, and atherosclerotic plaques most often remain stable. But it happens that the fibrous covering of the artery becomes fragile. Weakening of the arterial wall results in the crack of the endothelium. When it ruptures, a clot will suddenly block the artery. This complete occlusion of the artery then leads to a myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Avoid pastries, candies, sweets, industrial cakes, food rich in industrial sugar, etc. Eat beneficial and living food every day such as crunchy vegetables, sprouted seeds, young cereal shoots and vegetable juices, and fresh grass juices, fresh seaweed, and consume as little meat as possible. These and many more healthy lifestyles will help to fight against traces of atherosclerosis
References
1. Tamminen M, Mottino G, Qiao JH, Breslow JL, Frank JS. Ultrastructure of early lipid accumulation in apoE-deficient mice. Arterioscl. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999;19:847–853. [PubMed]
2. Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993;362:801–809.[Google Scholar]