Did you know that turmeric and black pepper are condiments that add flavor to your dish AND help reduce inflammation in your body? It has been a part of ancient medicine and is still in the health industry picture.
Many wellness brands that work with natural ingredients rely on turmeric and black pepper as their primary ingredients when it comes to joint health.
In this blog, we are going to dive deeper into the world of turmeric and black pepper and understand its health benefits specifically for arthritis. We will also understand the main causes of arthritis and ways to use these condiments as a solution.
What Are The Causes Of Arthritis?
Arthritis is fairly an old-age thing, but many young adults are also suffering from this condition. The main causes of arthritis are as below.
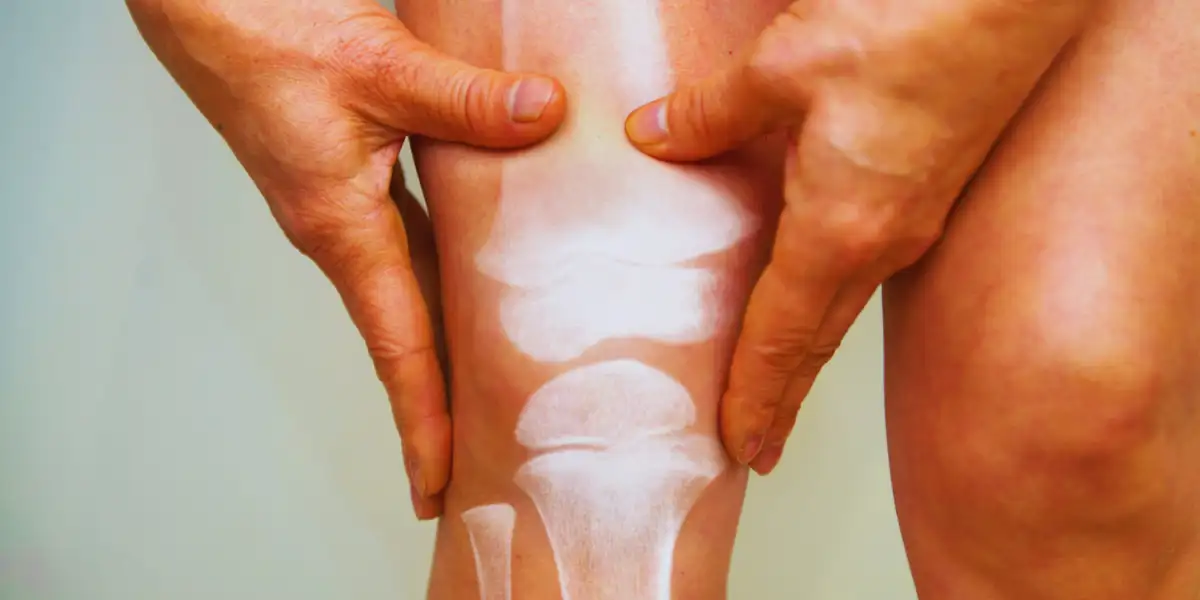
- Long overuse of the joints
- Obesity
- Auto-immune disorder
- Arthritis running in the family history
- Severe injury
- Weakness in muscles
- Exposure to viruses or toxins
- Gout
Connection Of Turmeric And Black Pepper With Arthritis
Turmeric and black pepper are both powerful spices, but when it comes to health, they have the power-pack performance stored in for you. Be it individually, or playing in combination, these two condiments can play an important role in joint health.
Active Compounds Present In Turmeric And Black Pepper
Turmeric comes from a long line of ginger family that contains curcumin as their active compound. This active compound has anti-inflammatory and antioxidants present in it which works as a natural healing ingredient.
Since arthritis depends on the level of inflammation present in your body, curcumin helps to manage the conditions by far.
So, it is safe to say that turmeric, the golden spice, has the magical powers to reduce the inflammation in your muscles and give relief from joint pain.
Some studies have concluded that the levels of pain that can be overcome by the daily use of turmeric and reduce the symptoms of arthritis.
Black pepper, on the other hand, has an active compound called Piperine. This is a highly bioavailable ingredient that works in favor of the absorption of important required minerals and vitamins.
With bioavailability, it can also help in absorbing the substances that are beneficial to your health but cannot be processed easily by the human body.
To make proper utilization of turmeric, black pepper works towards soaking up all the goodness it has to offer for your body. Curcumin and piperine work more effectively when put together and can manage inflammation-related issues in your body.
Medical Research And Trials
As per the clinical trial, a group of people affected by rheumatoid arthritis, and Osteoarthritis were examined and compared with the pain relievers ibuprofen and diclofenac sodium.
The meta-analysis of the 8-12 weeks of two groups saw that turmeric has similar improvements in inflammation and works as an excellent pain reliever.
As a result, turmeric extracts and curcumin supplements are safe for consumption to alleviate pain and reduce the symptoms of arthritis.
Several studies also suggest that curcumin can help reduce systemic inflammation which is beyond arthritis. Conditions like hypertension, increased cholesterol, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, visceral obesity, and increased triglyceride levels can be treated with Curcumin.
Turmeric as a whole can fight off oxidative stress, improve insulin sensitivity, and blood pressure, and reduce inflammation.
The only drawback that the studies saw was that it has difficulty in absorption, which means it can get out of your body as soon as it gets in.
To maintain its performance streak, it needs to be blended with a bioavailable compound. The most effective bioavailable compound that works well with ancient medicine is Piperine, found in black pepper.
When the combination of curcumin and piperine is used, the bioavailability has shown an increase of 2000%.
Other health benefits of adding turmeric and black pepper to your routine include:
- Improves memory
- Enhanced skin health
- Controlled obesity
- Helps to fight off depression
- Manages diabetes
- Protects liver health
- Helps in digestion
Incorporating Turmeric And Black Pepper In Our Diet
As spices, many culinary dishes can accommodate turmeric and black pepper individually and combined to manage arthritis. Here are some of the ways that you can try to spice up your dishes with turmeric and black pepper.
Golden Milk
Golden milk famously known as “Haldi Doodh” is a traditional drink that helps to reduce pain naturally. Take a glass of milk and boil it on low flame. Add a pinch of turmeric and mix it well. Add sugar if you have a sweet tooth, and drink it.
Popcorn Smurf
Popcorn is a healthy snack that you need not worry about calories. While preparing popcorn, add a pinch of turmeric and a teaspoon of crushed black pepper. At last, add salt to taste, and your movie snack is ready!
Quinoa Based Salad
For your next salad-based recipe, cook the soaked quinoa with a pinch of turmeric and a teaspoon of powdered black pepper. Have all your veggies ready and in the mixing bowl.
Mix the quinoa base and salad thoroughly and top it with your choice of nuts. You can also add some cheese to add texture to it, but choose the one that suits your diet.
Spicy Hummus
For your next hummus recipe, add a pinch of turmeric, a teaspoon of powdered black pepper, and some cumin to it. This will not only elevate the flavor but also help with reducing pain and managing the symptoms of arthritis.
Conclusion
Turmeric and black pepper are commonly found in condiments in every household. Natural medicine works best when the ingredients are free from chemicals.
Make sure to buy these condiments from an authentic brand that works with organic ingredients. Also, do not go overboard with the spices as they can affect you negatively.
You can also try meditation and light stretches to keep the arthritis pain away. Start slow and gradually increase the sets or new exercises for your routine. Give your joints the love and care that they deserve!
References:
- Turmeric. (2016).
https://nccih.nih.gov/health/turmeric/ataglance.htm - Akhtar, N., & Haqqi, T.M. (2012, June). Current neutraceuticals in the management of osteoarthritis: A review. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease, 4(3), 181-297. Retrieved from
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400101/